new jersey v tlo amendment
TLO Case Brief - Rule of Law. 325 January 15 1985 Decided.
A teacher found TLO.

. 63 decision for New Jerseymajority opinion by Byron R. Or do students not have a reasonable expectation of privacy while in school. Supreme Court ruled in New Jersey v.
Took her cause to the new jersey supreme court which later found that the search was unreasonable. Who was involved in NJ v TLO. Questions to Consider.
From a judge before. TLO holding that public school administrators can search a students belongings if they have a reasonable suspicion of criminal activity. Was a juvenile court case TLO.
In addition to the previously argued question the Court requested that the parties. January 15 1985. Dealing with the authority of school officials to search students possessions at school.
Review of the evolution of the warrant theory under the fourth amendment indicates that the language of the amendment prohibits the issuance of a warrant without probable cause. The Fourth Amendment in public schools. Reasoning The Fourth Amendment applies to public school officials not only police The Court reasoned the Fourth Amendment applies to government action or the actions of a sovereign authority.
Constitution protects people from unreasonable searches and. Reasonable the New Jersey Supreme Courts decision to exclude that evidence from TLOs juvenile delinquency proceedings on Fourth Amendment grounds was erroneous. The case originated in Piscataway New Jersey where in 1980 a teacher at the local public high school stumbled upon two girls smoking in a bathroom.
CERTIORARI TO THE SUPREME COURT OF NEW JERSEY No. TLO high school students are only partially protected from illegal searches and seizures. TLO decided in 1985 the Supreme Court took up the issue of when school officials can search students personal belongings.
The Fourth Amendment to the US. Syllabus NEW JERSEY v. The Fourth Amendment in public schools.
On January 15 1985 the US. The 4th Amendment prohibits the unlawful search and seizure of resident belonging to citizens of the United States of America. TLO was a case appealed to the Supreme Court in 1984 involving the search of a high school student for contraband after she was caught smoking.
School officials need not obtain a warrant before searching a student who is under their authority. The following statutory regulations were employed with regard to the New Jersey v. On January 15 1985 the US.
The court sided with the schooland TLO. After the original oral argument in March of 1984 the Supreme Court restored the case to the calendar for reargument. The Fourth Amendment to the constitution protects United States citizens from unreasonable searches and seizures.
This amendment also defines the rights of privacy awarded to citizens of the United States. The search resulting in the discovery of the evidence of marijuana dealing by the student was reasonable. She was charged as a juvenile for the drugs paraphernalia found in the search.
And another student smoking cigarettes in the girls restroom in the school building in violation of school rules. The case of New Jersey v. Tracy Lois Odem argued that her Fourth Amendment rights against unreasonable searches had been violated.
New Jersey v. SUPREME COURT OF THE UNITED STATES 469 US. As a result of the Courts holding in New Jersey v.
Although the State had argued in the Supreme Court of New Jersey that the search of TLOs purse did not violate the Fourth Amendment the petition for certiorari raised only the question whether the exclusionary rule should operate to bar consideration in juvenile delinquency proceedings of evidence unlawfully seized by a school official without the involvement of law. Do students have Fourth Amendment protections against unreasonable searches and seizures by teachers and school staff. This Fourth Amendment activity is based on the landmark Supreme Court case New Jersey v.
Supreme Court ruled in New Jersey v. I On March 7 1980 a teacher at Piscataway High School in Middlesex County N. TLO holding that public school administrators can search a students belongings if they have a reasonable suspicion of criminal activity.
325 1985 Argued March 28 1984 Reargued October 2 1984 Decided January 15 1985 JUSTICE WHITE delivered the opinion of the Court. We granted certiorari in this case to examine the appropriateness of the exclusionary rule as a remedy for searches carried out in violation of the Fourth Amendment by public school authorities. Background and Facts.
Supreme Court ruled in New Jersey v. Argued March 28 1984-Reargued October 2 1984-Decided January 15 1985 A teacher at a New Jersey high school upon discovering respondent then a 14-year-old freshman and her companion smoking cigarettes in a. TLO holding that public school administrators can search a students belongings if they have a.
J discovered two girls smoking in a lavatory. The side of the Supreme Court. New Jersey V.
JUSTICE WHITE delivered the opinion of the Court. The teacher brought the two students to a school administrator who questioned each of them. On January 15 1985 the US.
Seizures This means that police officers need to have a. TLO holding that public school administrators can search a students belongings if they have a reasonable suspicion of criminal activity. Our forefathers recognized the harm and abuses that occurred in the colonies to innocent people by the British and they made sure to write protections into the US.
The right of the people to be secure in their persons houses papers and effects against unreasonable searches and seizures shall not be violated and no warrants shall issue but upon probable cause supported by oath or affirmation and part. Was a 14-year-old female student at a New Jersey high school. United States Courts.
In New Jersey v. Supreme Court ruled in New Jersey v. The Fourth Amendment in public schools.
Why does the Court say the Fourth Amendment applies to students in schools. Our forefathers recognized the harm and abuses that occurred in the colonies to innocent people by the British and they made sure to write protections into the US. On January 15 1985 the US.
Tlo The Fourth Amendment to the constitution protects United States citizens from unreasonable searches and seizures. One of the two girls was the respondent T. The Supreme Court of New Jersey overruled the Appellate Division.
New Jersey v TLO. New Jersey v. The Appellant Division affirmed the trial courts finding there was no Fourth Amendment violation.
6 For example it applies to civil as well as criminal authorities such as building inspectors 7 OSHA inspectors 8 and firemen. Accordingly the judgment of the Supreme Court of New Jersey is reversed.

New Jersey Vs T L O By Cassie Kluck
N J V Tlo Civil Rights Or Civil Liberties Supreme Court Cases
Fourth Amendment Basics Jurisfusion Com

The Supreme Court Precedent Cases New Jersey V T L O 1985 Youtube

New Jersey Vs T L O By Cassie Kluck

Ppt Nj V Tlo Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 2583808

Why The Principal Can Search Your Purse New Jersey V T L O Youtube

Supreme Court Case New Jersey V Tlo Fourth Amendment By The History Source

You Can T Search My Bag That S Violating My Rights Triton Voice

New Jersey Vs Tlo Explained In Five Minutes Us History Review Youtube
New Jersey V T L O By Karmel Tanner On Prezi Next
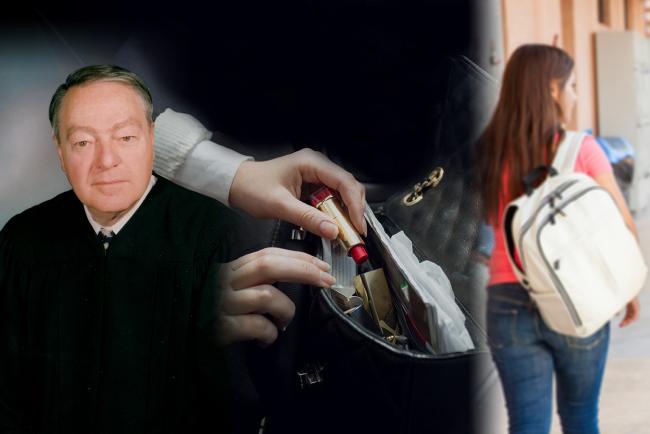

Triton Voice New Jersey Vs T L O

Amazon Com New Jersey V T L O Drug Searches In Schools Landmark Supreme Court Cases 9780894909696 Persico Deborah A Books

New Jersey V Tlo Trevor B Akilia R Facts About The Case In 1980 A Teacher At Piscataway In Nj Discovered Two Girl Smoking In A Restroom This Was Ppt Download

New Jersey V T L O Screen 2 On Flowvella Presentation Software For Mac Ipad And Iphone

New Jersey V T L O Screen 4 On Flowvella Presentation Software For Mac Ipad And Iphone

